TAPI ARCHITECTURE:
you'll learn how the Telephony API is organized and how its
various function calls are used to provide TAPI services to Windows applications. You'll
learn about the four different levels of TAPI services:
 | Assisted Telephony-This is the simplest form of TAPI service. |
 | Basic Telephony-This provides basic in- and outbound telephony services for a
single-line phone. |
 | Supplemental Telephony-This provides advanced telephone services such as hold,
park, conference, and so on, to single and Multiline phones. |
 | Extended Telephony-This provides a direct interface between Windows programs and
vendor-specific TAPI services. |
You'll also learn how these levels of service are implemented using API calls and how
they work together to provide complete TAPI services, from a simple Dial button, through handling inbound and outbound calls, to
acting as a switchboard in a Multiline setting, and finally to providing access to
vendor-specific features of telephony cards.
When you complete this chapter you'll understand how the Telephony API is organized and
how you can use it to add telephony services to your Windows applications.
The simplest form of TAPI service is Assisted Telephony. Under the Assisted
Telephony interface, programmers can place outbound calls and check the current dialing
location of the workstation. This type of telephony service can be used to provide a
simple Dial button to existing applications or add
dialing capabilities to new applications that will use telephony as an added service.
In fact, the Assisted Telephony model only provides access for programs to request the placement
of an outbound call. The actual dialing of the call is handled by another Windows/TAPI
application. The default application is DIALER.EXE.
This application ships with the Windows TAPI SDK and is part of the Windows 95 operating
system.
There are two API calls used to provide Assisted TAPI services. Table shows the
two calls, their parameters, and descriptions of what they do and how they can be used.
The Assisted Telephony API.
| API Call |
Parameters |
Comments |
| TapiRequestMakeCall |
DestAddress, AppName,
CalledParty, Comment
|
Use this function to request an outbound call placement. Only the DestAddress is required. |
| TapiGetLocationInfo |
CountryCode, CityCode |
Use this function to return the current country code and city code of
theworkstation. These values are stored in the TELEPHON.INIfile.
|
The TapiRequestMakeCall has four parameters. Only
the DestAddess is required. The DestAddress is a string of numbers that represents the
telephone number to dial. For example, "999-555-1212" is a valid DestAddress in the United States format. The AppName parameter is the name of the application that requested
the TAPI service. This would be the name of your application. The CalledParty
is a string that represents the name of the person you are calling. This information could
be used by the DIALER.EXE application to log the
person called. The Comment parameter could contain a
string of text describing the reason for the call.
The TapiGetLocation function returns two
parameters: the CountryCode and CityCode of the current location set by the Windows control
panel TAPI applet. These two parameters are stored in the TELEPHON.INI
file in the Windows folder of the workstation. The country code is a value used to place
out-of-country calls. The country code for the United States is "1." The CityCode is known as the area code in the United States.
The combination of the country code and the city code is used to determine how the TAPI
dialer will place the requested call.
For example, if the requested call contained "1-312-555-1212" and the current
workstation location indicated a country code of "1" and a city code of
"312," then the TAPI DIALER.EXE program
would attempt to place the call without including the country or city codes:
"555-1212." If, however, the requested call contained "43-80-12 33 45"
then the DIALER program would assume that the user
was attempting to place an out-of-country call and would use the appropriate dialing
prefixes.
Basic Telephony is the next level up in the TAPI service model. Basic Telephony
function calls allow programmers to create applications that can provide basic in- and
outbound voice and data calls over a single-line analog telephone. The analog phone line
most often used for this level of service is often referred to as a POTS or
Plain Old Telephone Service line. The Basic Telephony API set can also be used with
more sophisticated lines such as T1, ISDN, or digital lines. However, the added features
of these advanced line devices (such as call forwarding, park, hold, conference, and so
on) are not available when using the Basic Telephony API set.
The Basic Telephony level of service focuses on the use of a line device as a
means of transporting information from one place to the next. A line device to TAPI can be
a handset, a fax board, a data modem, a telephony card, or any other physical device that
can be attached to a telephone line, But it is treated as a virtual device, not a physical
one.
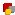
Line devices are not associated directly with any physical telephone line. This way,
TAPI can "see" multiple TAPI devices on the same machine (data modem, handset,
and fax board) while there is only one physical telephone line attached to the workstation
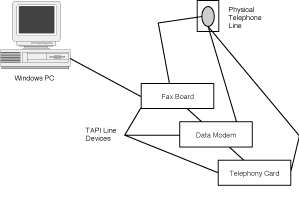
One of the primary functions of the TAPI interface is to handle multiple TAPI service
requests from the workstation. It is possible that several applications running on the
workstation may request TAPI services at some time. The call control application (DIALER.EXE) accepts each request and places them in a queue for
processing in the requested order.
The Basic Telephony service model has several API calls for handling and fulfilling
service requests. These calls can be collected into logical groups:
 | Basic line-handling calls handle the initialization and opening and closing of
TAPI lines. |
 | Line settings and status calls handle the reading and writing of various
parameter values that control the behavior of the line device. |
 | Outbound and inbound functions handle the details of placing an outbound voice or
data call and answering an inbound voice or data call. |
 | Addressing functions handle the details of recognizing, translating, and/or
building telephone "addresses" or dialing strings. |
 | Miscellaneous features handle other TAPI-related functions, such as managing
call-monitoring privileges and manipulating call handles. |
Table shows the Basic Telephony API calls, sorted by functional group, along with a
short description of their use.
The Basic Telephony line device API set.
| Function Group |
API Call |
Description |
| Basic line-handling |
lineInitialize |
Initializes the Telephony API line abstraction for use by the invoking
application. |
| |
lineShutdown |
Shuts down the application's use of the Telephony API line. |
| |
lineNegotiateAPIVersion |
Allows an application to negotiate an API version to use. |
| |
lineOpen |
Opens a specified line device for providing subsequent monitoring and/or
control of the line. |
| |
lineClose |
Closes a specified opened line device. |
| |
lineDrop |
Disconnects a call, or abandons a call attempt in progress. |
| |
lineDeallocateCall |
De-allocates the specified call handle. |
| Line settings and status |
lineGetDevCaps |
Returns the capabilities of a given line device. |
| |
lineGetDevConfig |
Returns the configuration of a media stream device. |
| |
lineGetlineDevStatus |
Returns the current status of the specified open line device. |
| |
lineSetDevConfig |
Sets the configuration of the specified media stream device. |
| |
lineSetStatusMessages |
Specifies the status changes for which the application wants to be
notified. |
| |
lineGetStatusMessages |
Returns the application's current line and address status message
settings. |
| |
lineGetID |
Retrieves a device ID associated with the specified open line, address, or
call. |
| |
lineSetNumRings |
Indicates the number of rings after which inbound calls are to be
answered. |
| |
lineGetNumRings |
This function returns the minimum number of rings requested with lineSetNumRings. |
| |
lineGetIcon |
Allows an application to retrieve an icon for display to the user. |
| |
lineConfigDialog |
Causes the provider of the specified line device to display a dialog that
allows the user to configure parameters related to the line device. |
| Inbound and outbound calls |
lineMakeCall |
Makes an outbound call and returns a call handle for it. |
| |
lineDial |
Dials (parts of one or more) dialable addresses. |
| |
lineAnswer |
Answers an inbound call. |
| Addresses |
lineGetAddressCaps |
Returns the telephony capabilities of an address. |
| |
lineGetAddressStatus |
Returns the current status of a specified address. |
| |
lineGetAddressID |
Retrieves the address ID of an address specified using an alternate
format. |
| |
lineTranslateAddress |
Translates between an address in canonical format and an address in
dialable format. |
| |
lineSetCurrentLocation |
Sets the location used as the context for address translation. |
| |
lineSetTollList |
Manipulates the toll list. |
| |
lineGetTranslateCaps |
Returns address translation capabilities. |
| Miscellaneous features |
lineGetCallInfo |
Returns mostly constant information about a call. |
| |
lineGetCallStatus |
Returns complete call status information for the specified call. |
| |
lineSetAppSpecific |
Sets the application-specific field of a call's information structure. |
| |
LineRegisterRequest ÂRecipient
|
Registers or de-registers the application as a request recipient for the
specified request mode. |
| |
lineGetRequest |
Gets the next request from the Telephony DLL. |
| |
lineSetCallPrivilege |
Sets the application's privilege to the privilege specified. |
| |
lineHandoff |
Hands off call ownership and/or changes an application's privileges to a
call. |
| |
lineGetNewCalls |
Returns call handles to calls on a specified line or address for which the
application does not yet have handles. |
| |
lineGetConfRelatedCalls |
Returns a list of call handles that are part of the same conference call
as the call specified as a parameter. |
Along with the extensive API set for Basic Telephony, the TAPI model defines several
data structures that are used to pass information between TAPI and the requesting
application. The layout of the structures contains variable as well as fixed data. This
allows the API set to contain information of indeterminate length without prior knowledge
of the contents of the structure.
In order to handle variable-length structures, the defined data structures contain
fields that indicate the total size needed to fill in all variable data (dwNeededSize) along with the total size used by TAPI when
filling in the structure (dwUsedSize). Listing
shows how this looks in the LINECALLLIST
structure.

Viewing the LINECALLLIST structure.
typedef struct linecalllist_tag {
DWORD dwTotalSize;
DWORD dwNeededSize;
DWORD dwUsedSize;
DWORD dwCallsNumEntries;
DWORD dwCallsSize;
DWORD dwCallsOffset;
} LINECALLLIST, FAR *LPLINECALLLIST;

The dwTotalSize field is first set by the calling
application to tell TAPI how much memory has been allocated for the structure. If TAPI
cannot fill in all values without running out of allocated space, an error is returned and
it is the job of the requesting application to re-allocate space and make the call again.
Along with the total size and total needed fields, each variable-length structure has a
fixed portion and a variable portion. The fixed portion contains values that indicate the
size of the variable-length field and the offset (from the start of the structure) at
which the field is located. Note the fields dwCallsSize
and dwCallsOffset in the LINECALLLIST
structure shown in Listing 23.1.
Table shows the list of data structures used by the Basic Telephony API set along with
short descriptions of their use.
The Basic Telephony API line device structures.
| Structure |
Description |
| LINEADDRESSCAPS |
Describes the capabilities of a specified address. |
| LINEADDRESSSTATUS |
Describes the current status of an address. |
| LINECALLINFO |
Contains information about a call. |
| LINECALLLIST |
Describes a list of call handles. |
| LINECALLPARAMS |
Describes parameters supplied when making calls using lineMakeCall. |
| LINECALLSTATUS |
Describes the current status of a call. |
| LINECARDENTRY |
Describes a calling card. |
| LINECOUNTRYENTRY |
Provides the information for a single country entry. |
| LINECOUNTRYLIST |
Describes a list of countries. |
| LINEDEVCAPS |
Describes the capabilities of a line device. |
| LINEDEVSTATUS |
Describes the current status of a line device. |
| LINEDIALPARAMS |
Specifies a collection of dialing-related fields. |
| LINEEXTENSIONID |
Describes an extension ID. Extension IDs are used to identify service
provider-specific extensions for line devices. |
| LINEFORWARD |
Describes an entry of the forwarding instructions. |
| LINEFORWARDLIST |
Describes a list of forwarding instructions. |
| LINEGENERATETONE |
Contains information about a tone to be generated. |
| LINELOCATIONENTRY |
Describes a location used to provide an address translation context. |
| LINEMEDIACONTROLCALLSTATE |
Describes a media action to be executed when detecting transitions into
one or more call states. |
| LINEMEDIACONTROLDIGIT |
Describes a media action to be executed when detecting a digit. |
| LINEMEDIACONTROLMEDIA |
Describes a media action to be executed when detecting a media-mode
change. |
| LINEMEDIACONTROLTONE |
Describes a media action to be executed when a tone has been detected. |
| LINEMONITORTONE |
Describes a tone to be monitored. |
| LINEPROVIDERENTRY |
Provides the information for a single-service provider entry. |
| LINEPROVIDERLIST |
Describes a list of service providers. |
| LINEREQMAKECALL |
Describes a tapiRequestMakeCall
request. |
| LINETERMCAPS |
Describes the capabilities of a line's terminal device. |
| LINETRANSLATECAPS |
Describes the address translation capabilities. |
| LINETRANSLATEOUTPUT |
Describes the result of an address translation. |
The Telephony API uses Windows messages to communicate with the requesting application.
When the requesting application first performs a LineInitialize
function, a callback function address must be supplied. All messages are then sent to this
callback function.
Each message returns the same set of parameters. The first is the relevant handle.
Usually this is the call handle, but it may also be a line handle. The second parameter is
the callback instance value. This value will always be the instance handle of the current
running application. The next three values vary depending on the message. One or more of
these return values will contain non-zero data. Table 23.3 contains a list of the Basic
Telephony messages, their parameters, and short descriptions.
Basic Telephony line device messages.
| Message |
Parameters |
Description |
| LINE_ADDRESSSTATE |
dwDevice = hLine;
dwCallbackInstance =
Callback;
dwParam1 = idAddress;
dwParam2 = AddressState;
dwParam3 = (DWORD) 0;
|
Sent when the status of an address changes on a line that is currently
open by the application. The application can invoke lineGetAddressStatusto
determine the current status of the address. |
| LINE_CALLINFO |
dwDevice = hCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = CallInfoState;
dwParam2 = (DWORD) 0;
dwParam3 = (DWORD) 0; |
Sent when the call information about the specified call has changed. The
application can invoke lineGetCallInfo to determine
the current call information. |
| LINE_CALLSTATE |
dwDevice = hCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = CallState;
dwParam2 =
CallStateDetail;
dwParam3 =
CallPrivilege; |
Sent when the status of the specified call has changed. Several such
messages will typically be received during the lifetime of a call. |
| LINE_CLOSE |
dwDevice = hLine;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = (DWORD) 0;
dwParam2 = (DWORD) 0;
dwParam3 = (DWORD) 0; |
Sent when the specified line device has been forcibly closed. The line
device handle or any call handles for calls on the line are no longer valid once this
message has been sent. |
| LINE_CREATE |
dwDevice = 0;
dwCallbackInstance = 0;
dwParam1 = idDevice;
dwParam2 = 0;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent to inform the application of the creation of a new line device. |
| LINE_DEVSPECIFIC |
dwDevice = hLineOrCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 =
DeviceSpecific1;
dwParam2 =
DeviceSpecific2;
dwParam3 =
DeviceSpecific3; |
Sent to notify the application about device-specific events occurring on a
line, address, or call. The meaning of the message and the interpretation of the
parameters is device specific. |
| LINE_DEVSPECIFICFEATURE |
dwDevice = hLineOrCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 =
DeviceSpecific1;
dwParam2 =
DeviceSpecific2;
dwParam3 =
DeviceSpecific3; |
Sent to notify the application about device-specific events occurring on a
line, address, or call. The meaning of the message and the interpretation of the
parameters is device specific. |
| LINE_GATHERDIGITS |
dwDevice = hCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 =
GatherTermination;
dwParam2 = 0;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent when the current buffered digit-gathering request has terminated or
is canceled. The digit buffer may be examined after this message has been received by the
application. |
| LINE_GENERATE |
dwDevice = hCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 =
GenerateTermination;
dwParam2 = 0;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent to notify the application that the current digit or tone generation
has terminated. Note that only one such generation request can be in progress on a given
call at any time. This message is also sent when digit or tone generation is canceled. |
| LINE_LINEDEVSTATE |
dwDevice = hLine;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = DeviceState;
dwParam2 =
DeviceStateDetail1;
dwParam3 =
DeviceStateDetail2 |
Sent when the state of a line device has changed. The application can
invoke lineGetLineDevStatus to determine the new
status of the line. |
| LINE_MONITORDIGITS
|
dwDevice = hCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = Digit;
dwParam2 = DigitMode;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent when a digit is detected. The sending of this message is controlled
with the lineMonitorDigits function. |
| LINE_MONITORMEDIA
|
dwDevice = hCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = MediaMode;
dwParam2 = 0;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent when a change in the call's media mode is detected. The sending of
this message is controlled with the lineMonitorMedia function.
|
| LINE_MONITORTONE
|
dwDevice = hCall;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = dwAppSpecific;
dwParam2 = 0;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent when a tone is detected. The sending of this message is controlled
with the lineMonitorTones function. |
| LINE_REPLY
|
dwDevice = 0;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = idRequest;
dwParam2 = Status;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent to report the results of function calls that completed
asynchronously. |
| LINE_REQUEST
|
dwDevice = 0;
dwCallbackInstance =
hRegistration;
dwParam1 = RequestMode;
dwParam2 =
RequestModeDetail1;
dwParam3 =
RequestModeDetail2; |
Sent to report the arrival of a new request from another application. |
Supplemental
Telephony Services
The Supplemental Telephony functions provide advanced line device handling (conference,
park, hold, forward, and so on). Access to these advanced services is dependent on the
type of telephone line to which the workstation is connected. In other words, even if you
implement call forwarding functions within your TAPI application, these functions will
only work if call forwarding services are available on the telephone line provided by the
local telephone company.
The Supplemental Telephony functions also allow programmers to handle service requests
for multiple-line phones. You can use Supplemental Telephony to mange a physical handset
that has access to multiple physical lines
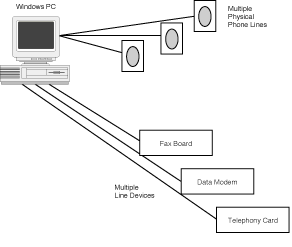
You can also use the Supplemental Telephony functions to manage multiple
handsets using one or more physical lines. Because TAPI "virtualizes" both line
and phone devices, there need not be a direct one-to-one correspondence between a defined
phone device and a defined line device. In this way you can use TAPI to create a
switchboard application to manage telephony services
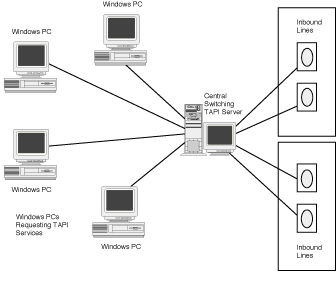
Supplemental Telephony also provides access to defining and manipulating
phone devices. To TAPI a phone device is any device that can accept or place calls. In
effect, you can register your workstation as a phone device. Then you can use resources on
your workstation to place or accept calls without the need of a handset or desktop phone.
Of course, in order to act successfully as a phone device, your workstation must have
audio input and output hardware.
The Supplemental API set for line devices adds advanced call control and other features
to the API library. The set can be divided into the following related groups of functions:
 | Digit and tone handling functions allow programmers to detect and generate digits
or tones along the phone line. This capability is needed to allow some systems to perform
advanced line operations such as forwarding, call holds, and so on. |
 | Advanced line-handling functions provide call acceptance, rejection, redirection,
and other operations. These are most useful in an environment where the phone line is
connected to a central switch instead of directly to the external telephone service
provider. |
 | Advanced call features functions provide Call Hold, Transfer, Park, Forward, and
Pickup capabilities. These functions only work if the telephone line supports the advanced
call features. |
 | Miscellaneous advanced features functions provide added features specific to TAPI
service requests, such as monitoring lines and setting call parameters. |
Table 23.4 shows all the Supplemental Telephony API functions for the advanced line
device features.
The Supplemental Telephony API set for line devices.
| Function Group |
API Call |
Description |
| Digit and tone handling |
lineMonitorDigits |
Enables or disables digit detection notification on a specified call. |
| |
LineGatherDigits |
Performs the buffered gathering of digits on a call. |
| |
LineMonitorTones |
Specifies which tones to detect on a specified call. |
| |
LineGenerateDigits |
Generates inband digits on a call. |
| |
LineGenerateTone |
Generates a given set of tones inband on a call. |
| Advanced call handling |
lineAccept |
Accepts an offered call and starts alerting both caller (ring-back) and
called party (ring). |
| |
LineRedirect |
Redirects an offering call to another address. |
| |
LineSecureCall |
Secures an existing call from interference by other events such as
call-waiting beeps on data connections. |
| |
LineCompleteCall |
Places a call completion request. |
| |
LineUncompleteCall |
Cancels a call completion request. |
| Call hold |
lineHold |
Places the specified call on hard hold. |
| |
LineUnhold |
Retrieves a held call. |
| Call transfer |
lineSetupTransfer |
Prepares a specified call for transfer to another address. |
| |
LineCompleteTransfer |
Transfers a call that was set up for transfer to another call, or enters a
three-way conference. |
| |
LineBlindTransfer |
Transfers a call to another party. |
| |
LineSwapHold |
Swaps the active call with the call currently on consultation hold. |
| Call conference |
lineSetupConference |
Prepares a given call for the addition of another party. |
| |
LinePrepareAddToConference |
Prepares to add a party to an existing conference call by allocating a
consultation call that can later be added to the conference call that is placed on
conference hold. |
| |
LineAddToConference |
Adds a consultation call to an existing conference call. |
| |
LineRemoveFromConference |
Removes a party from a conference call. |
| Call park |
linePark |
Parks a given call at another address. |
| |
LineUnpark |
Retrieves a parked call. |
| Call forwarding |
lineForward |
Sets or cancels call forwarding requests. |
| Call pickup |
linePickup |
Picks up a call that is alerting at another number. Picks up a call
alerting at another destination address and returns a call handle for the picked up call (linePickup can also be used for call waiting). |
| Miscellaneous advanced features |
lineSendUserUserInfo |
Sends user-to-user information to the remote party on the specified call
(ISDN only). |
| |
LineSetTerminal |
Specifies the terminal device to which the specified line, address events,
or call media stream events are routed. |
| |
LineSetCallParams |
Requests a change in the call parameters of an existing call. |
| |
LineMonitorMedia |
Enables or disables media mode notification on a specified call. |
| |
LineSetMediaControl |
Sets up a call's media stream for media control. |
| |
LineSetMediaMode |
Sets the media mode(s) of the specified call in its LINECALLINFO structure. |
The Supplemental Telephony API also provides function calls for the handling of phone
devices. To TAPI, any device that can place or accept calls can be a phone device. The
phone device API set allows programmers to invent their own phone devices in code. In
effect, you can create a virtual handset using the TAPI phone device. This allows properly
equipped workstations to act as single- or multiple-line phones in an office environment.
If your pc has appropriate audio input and output hardware (speakers, sound card,
microphone, and so on) and is connected to the telephone service, you can create a
"handset" using the phone device API set.
The Supplemental Telephony API set for phone devices can be divided into the following
function groups:
 | Basic phone-handling functions provide basic initialization and shutdown, opening
and closing a phone device, and ringing the open device. |
 | Phone settings and status functions allow programmers to read and write various
settings of the phone device such as volume, gain, hookswitch behavior, and so on. |
 | Physical display, data, button, and lamp functions can be used to read and write
display information to desktop units. Since TAPI can be used to support more than just pc
workstations, these functions allow a central TAPI program to monitor and update LCD
displays, to flash lamps, to change buttons labels, and to store and retrieve data from
desktop terminals. |
Table 23.5 shows all the Supplemental Telephony phone device API calls along with short
descriptions of their use.
Table 23.5. The Supplemental Telephony API for phone devices.
| Function Group |
API Call |
Description |
| Basic phone handling |
phoneInitialize |
Initializes the Telephony API phone device for use by the invoking
application. |
| |
phoneShutdown |
Shuts down the applica-tion's use of the phone Telephony API. |
| |
phoneNegotiateAPIVersion |
Allows an application to negotiate an API version to use. |
| |
phoneOpen |
Opens the specified phone device, giving the application either owner or
monitor privileges. |
| |
PhoneClose |
Closes a specified open phone device. |
| |
PhoneSetRing |
Rings an open phone device according to a given ring mode. |
| |
PhoneGetRing |
Returns the current ring mode of an opened phone device. |
| Phone settings and status |
phoneGetDevCaps |
Returns the capabilities of a given phone device. |
| |
PhoneGetID |
Returns a device ID for the given device class associated with the
specified phone device. |
| |
PhoneGetIcon |
Allows an application to retrieve an icon for display to the user. |
| |
PhoneConfigDialog |
Causes the provider of the specified phone device to display a dialog that
allows the user to configure parameters related to the phone device. |
| |
PhoneSetStatusMessages |
Specifies the status changes for which the application wants to be
notified. |
| |
PhoneGetStatusMessages |
Returns the status changes for which the application wants to be notified.
|
| |
PhoneGetStatus |
Returns the complete status of an open phone device. |
| |
PhoneSetHookSwitch |
Sets the hookswitch mode of one or more of the hook-switch devices of an
open phone device. |
| |
PhoneGetHookSwitch |
Queries the hookswitch mode of a hookswitch device of an open phone
device. |
| |
PhoneSetVolume |
Sets the volume of a hook-switch device's speaker of an open phone device.
|
| |
PhoneGetVolume |
Returns the volume setting of a hookswitch device's speaker of an open
phone device. |
| |
PhoneSetGain |
Sets the gain of a hookswitch device's mic of an open phone device. |
| |
PhoneGetGain |
Returns the gain setting of a hookswitch device's mic of an open phone
device. |
| Physical display, data, buttons, and lamps |
phoneSetDisplay |
Writes information to the display of an open phone device. |
| |
PhoneGetDisplay |
Returns the current contents of a phone's display. |
| |
PhoneSetButtonInfo |
Sets the information associated with a button on a phone device. |
| |
PhoneGetButtonInfo |
Returns information associated with a button on a phone device. |
| |
PhoneSetLamp |
Lights a lamp on a specified open phone device in a given lamp-lighting
mode. |
| |
PhoneGetLamp |
Returns the current lamp mode of the specified lamp. |
| |
PhoneSetData |
Downloads a buffer of data to a given data area in the phone device. |
| |
PhoneGetData |
Uploads the contents of a given data area in the phone device to a buffer.
|
Just as the line device API set has a series of data structures, the phone device set
also has related data structures. These structures are used to pass information between
the desktop program and the TAPI service provider.
The phone device structures most often used are the PHONECAPS
and PHONESTATUS structures. Table 23.6 shows all the
phone device structures along with brief descriptions of their use.
Table 23.6. The Supplemental Telephony phone device structures.
| Structure |
Description |
| PHONEBUTTONINFO |
Contains information about a button on a phone device. |
| PHONECAPS |
Describes the capabilities of a phone device. |
| PHONEEXTENSIONID |
Describes an extension ID. Extension IDs are used to identify service
provider-specific extensions for phone device classes. Used mostly for Extended Telephony.
|
| PHONESTATUS |
Describes the current status of a phone device. |
| VARSTRING |
Used for returning variably sized strings. It is used both by the line
device class and the phone device class. |
The Supplemental Telephony phone device also uses a callback function to register a
function address to receive Windows messages. This callback address is established during
the phoneInitialize API call.
| Note |
The fact that TAPI uses callbacks for messages means that any high-level languages such
as Visual Basic must use either a DLL or OCX or establish the callback link or use some
other tool that can capture windows messages. A sample OCX is included on the CD-ROM that
ships with this book. This OCX is used throughout the book to show how you can link Visual
Basic and other VBA-compliant languages to TAPI services.
|
Each message returns the same set of parameters. The first is the handle of the phone
device. The second parameter is the callback instance value. This value will always be the
instance handle of the current running application. The next three values vary depending
on the message. One or more of these return values will contain non-zero data. Table 23.7
contains a list of the Basic Telephony messages, their parameters, and short descriptions.
Table 23.7. The Supplemental Telephony phone device messages.
| Message |
Parameters |
Description |
| PHONE_BUTTON |
hPhone = hPhoneDevice;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 =
idButtonOrLamp;
dwParam2 = ButtonMode;
dwParam3 = ButtonState; |
Sent to notify the application that button press monitoring is enabled if
it has detected a button press on the local phone. |
| PHONE_CLOSE |
hPhone = hPhoneDevice;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = 0;
dwParam2 = 0;
dwParam3 = 0; |
Sent when an open phone
device has been forcibly
closed as part of resource
reclamation. The device handle is no longer valid once this message has been sent. |
| PHONE_CREATE |
hPhone = hPhoneDev;
dwCallbackInstance = 0;
dwParam1 = idDevice;
dwParam2 = 0;
dwParam3 = 0; |
This message is sent to inform applications of the creation of a new phone
device. |
| PHONE_DEVSPECIFIC |
hPhone = hPhoneDevice;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = DevSpecific1;
dwParam2 = DevSpecific2;
dwParam3 = DevSpecific3; |
This message is sent to notify the application about device- specific
events occurring at the phone. The meaning of the message and the interpretation of the
parameters is defined by the hardware vendor. |
| PHONE_REPLY |
hPhone = 0;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = idRequest;
dwParam2 = Status;
dwParam3 = 0; |
This message is sent to report the results of a function call that
completed asynchronously. |
| PHONE_STATE |
hPhone = hPhoneDevice;
dwCallbackInstance =
hCallback;
dwParam1 = PhoneState;
dwParam2 =
PhoneStateDetails;
dwParam3 = 0; |
The service provider sends this message to an application's callback
function whenever the status of a phone device changes. |
The last level of Telephony services is Extended Telephony. Extended Telephony service
allows hardware vendors to define their own device-specific functions and services and
still operate under the TAPI service model. By adding a small set of extended service API
functions, Microsoft allows hardware vendors to continue to provide unique services not
previously defined by TAPI. The TAPI model defines both line and phone device API calls
for Extended Telephony.
Table 23.8 shows the Extended Telephony API set along with short descriptions of their
use.
Table 23. 8. The Extended Telephony API set.
| Function Group |
API Call |
Description |
| Extended Line service |
lineNegotiateExtVersion |
Allows an application to use with the negotiate an extension version to
specified line device. |
| |
lineDevSpecific |
Device-specific escape function. |
| |
lineDevSpecificFeature |
Device-specific escape function to allow sending switch features to the
switch. |
| Extended Phone service |
phoneNegotiateExtVersion |
Allows an application to negotiate an extension version to use with the
specified phone device. |
| |
phoneDevSpecific |
Device-specific escape function to allow vendor dependent extensions. |
The actual meaning and use of extended TAPI calls is defined by the service provider or
hardware vendor. Extended Telephony providers define the parameters of the calls and their
meaning, and publish this information to the programmer. The programmer can then check the
version information with the service provider before attempting to make an extended
service call.